40 homolougous structures
What are homologous structures? What are their functions? Homologous structures are not a type of evolution. Homologous structures are organs or skeletal elements of animals and organisms that, by virtue of their similarity, suggest their connection to a common ancestor. These structures do not necessarily look the same or have the same function. Cytoarchitecture, Topography, and Descending Supraspinal Projections in ... In contrast, most of the other expression domains of AmphiPax2/5/8 correspond to expression domains of vertebrate Pax2, Pax5 and Pax8 in structures that are probably homologous - support cells of ...
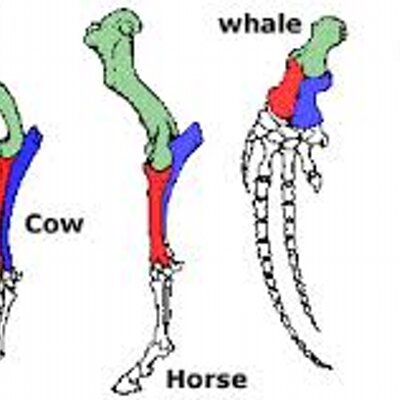
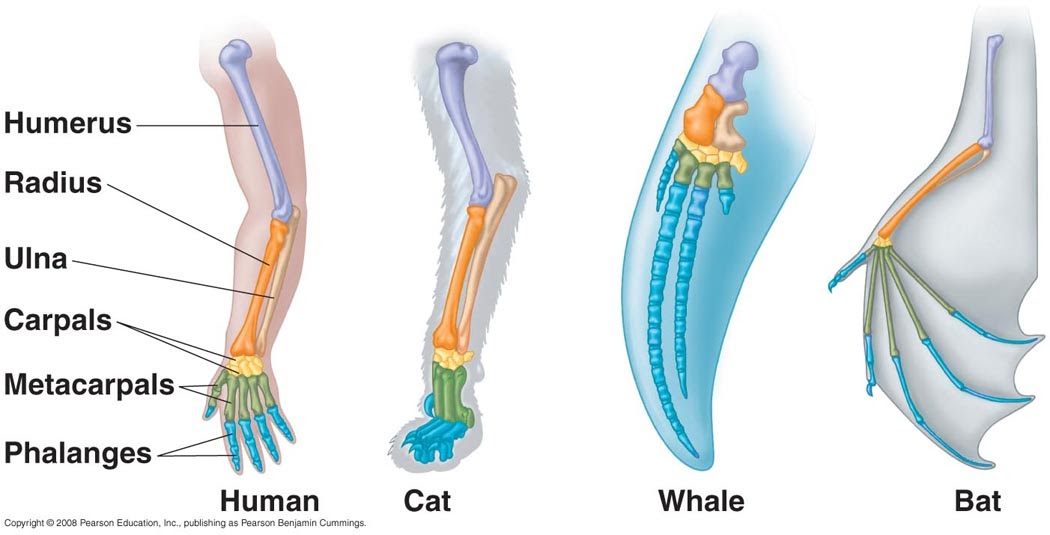
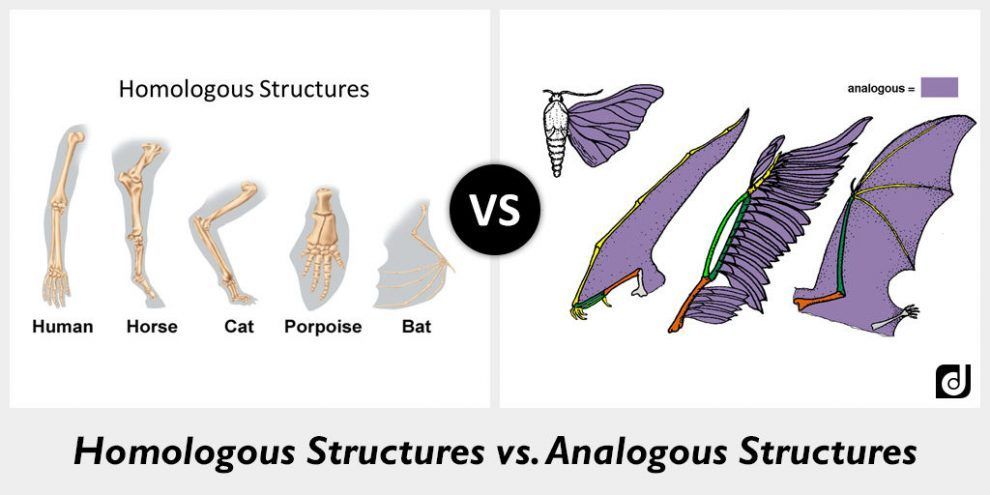
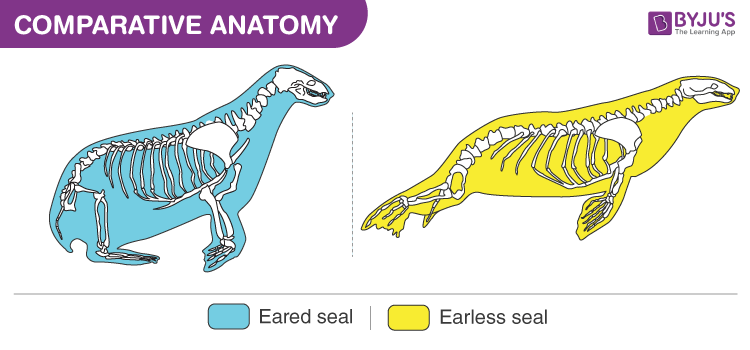
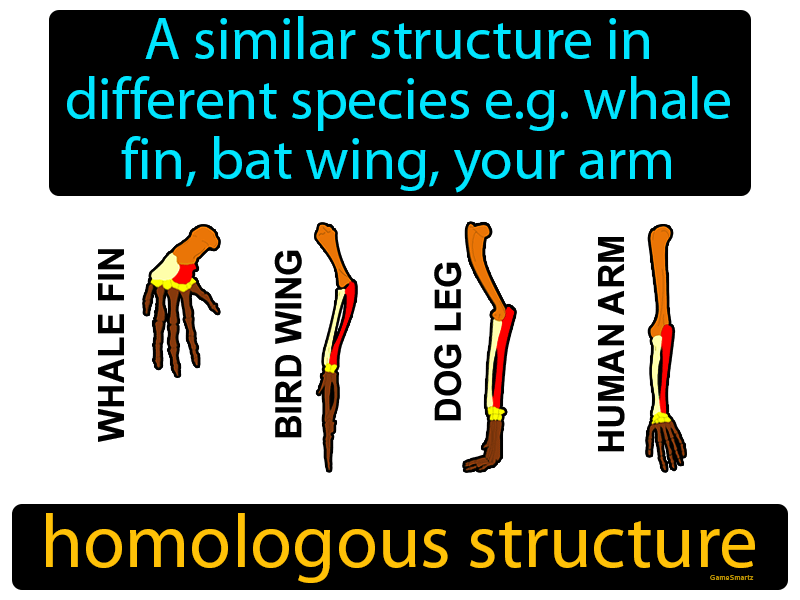
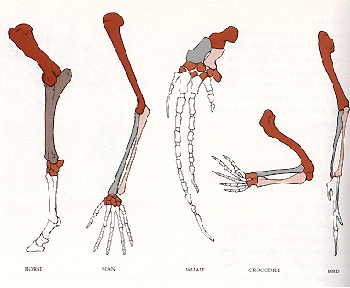
Difference Between Homologous and Analogous Structures - BYJUS An arm of a human, the leg of a dog or a flipper of a whale are all homologous structures. From wings in birds, bats and insects to fins in penguins and fishes are all analogous structures. These were a few differences between analogous and homologous structures. From this, we can conclude that the main difference between homologous and ...
Homolougous structures
Anatomy, Evolution, and Homologous Structures - ThoughtCo As time passed and technology advanced, homologous structures became more important in deciding the final placement on the phylogenetic tree of life . Linnaeus's taxonomy system places species into broad categories. The major categories from general to specific are kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. 10 Difference Between Homologous And Analogous Structures/Organs With ... A homologous structure is an organ or body part that appears in different animals and is similar in structure and location, but doesn't necessarily share the same purpose. This type of evolution is referred to as divergent evolution. An example of homologous structure is the forelimb of a frog and man seems to be built from same basic design ... Homologous Structures: Explanation, Examples, & Traits - Study.com Evolutionary biologists that study genetics of organisms noticed similarities in structures of these organisms even when the function was not the same. These structures are called homologous...
Homolougous structures. What is homologous structures? - Answers A homologous structures are structures that share an evolutionary ancestry. An example of homologous structures would be the bones in the arms of a human, the wings of a bat, and the legs of a dog. Homologous structures Flashcards | Quizlet Homologous structure Structures that are similar in different species of common ancestry Vestigial structure A structure that is present in an organism but no longer serves its original purpose Inherited Genetic markers Ancestor A relative who lived in the past Evolution Change over time Adaption A trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce Homologous and Analogous Structures Flashcards & Practice Test - Quizlet Terms in this set (15) Homologous Structures. structures in different species inherited from a common ancestor. Similar structure DIFFERENT function. EX- Horse and Human arms- similar in structure but have different function. Analogous Structures. body parts that share a common function but not structure. two species faced similar challenges ... Difference Between Homologous and Analogous Structures Homologous structures are part of the body of a species that are anatomically similar to the comparative part of another species. The homologous structures suggest that diverse species are derived from a common ancestor over time. Therefore, the anatomy of the homologous structures can be used as a fact to develop phylogenetic trees of life.
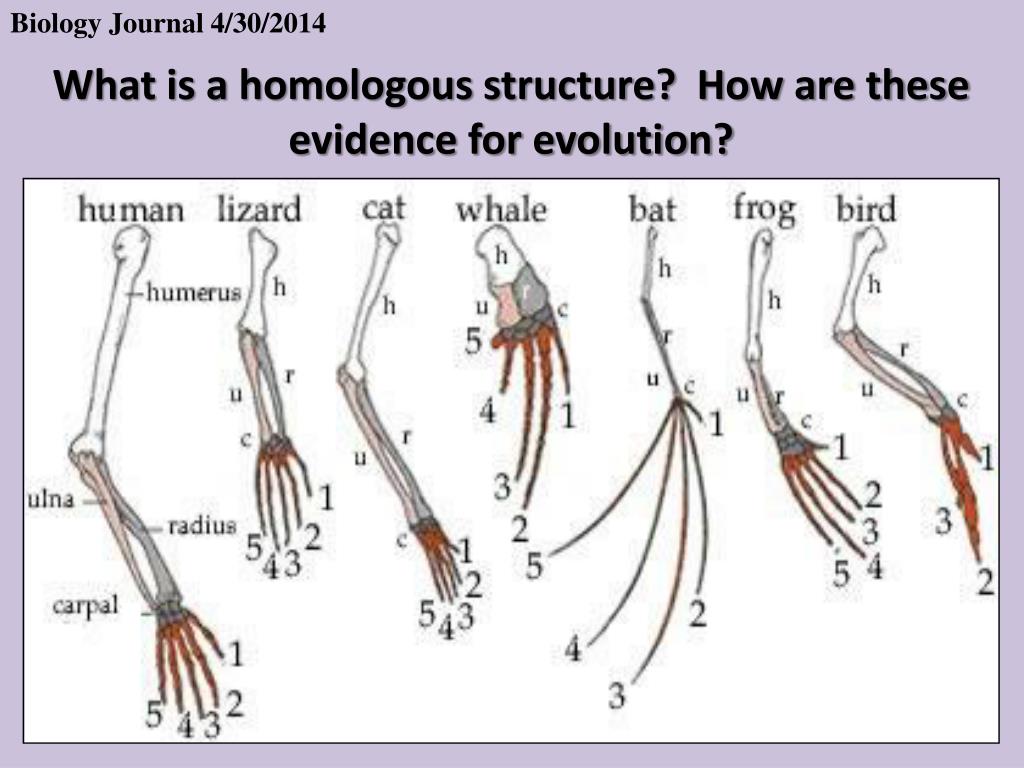
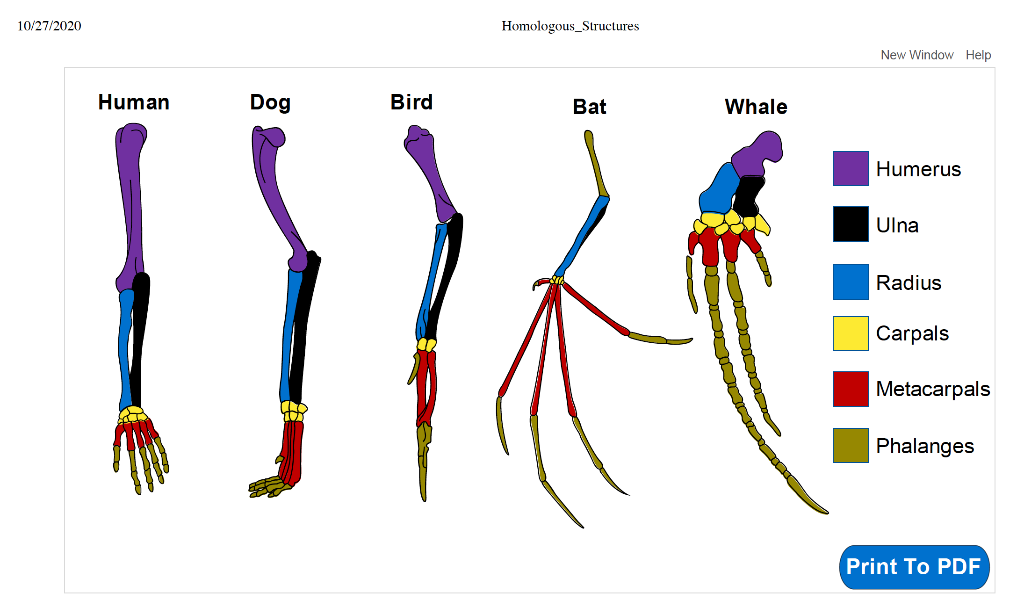
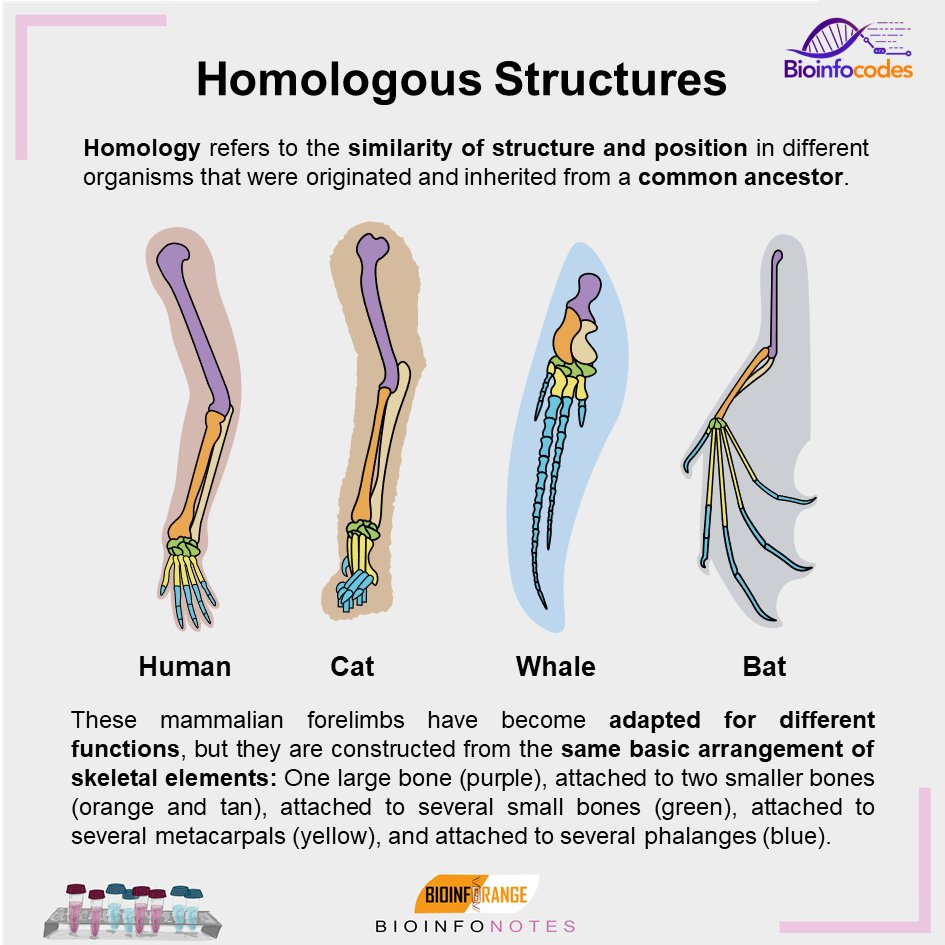
Homologous Structure Examples in Different Organisms - YourDictionary A dolphin's flipper, a bird's wing, a cat's leg, and a human arm are considered homologous structures. Whereas human beings have bones such as the humerus (upper arm), ulna and radius (forearm), carpals (wrist bones), metacarpals (hand bones), and phalanges (fingers), these features appear as similar bones in form in the other animals. Homologous and Analogous Structures: What's the Difference? - PrepScholar Homologous structures are similar structures in related organisms. The most important thing to remember about homologous structures is that they share common ancestry. In other words, only organisms that are somehow related to each other can have homologous structures. For example, a chimpanzee's arm and a human's arm are homologous structures. Examples of Homologous Structures That Reveal Our Shared Ancestry Homologous structures are structurally and functionally similar and derived from a common ancestor; whereas, analogous structures have similar functions but are not descended from a common ancestor. The term homology was coined in the year 1656. It is derived from the Greek words homos, meaning 'same' and logos, meaning 'relation'. Homologous and analogous structures (with examples) The homologous structure They are parts of a biological organism that share a common ancestor, while analogous ones perform similar functions. When comparing two processes or structures, we can assign them as homologues and analogues. These concepts gained popularity after the emergence of evolutionary theory, and their recognition and ...
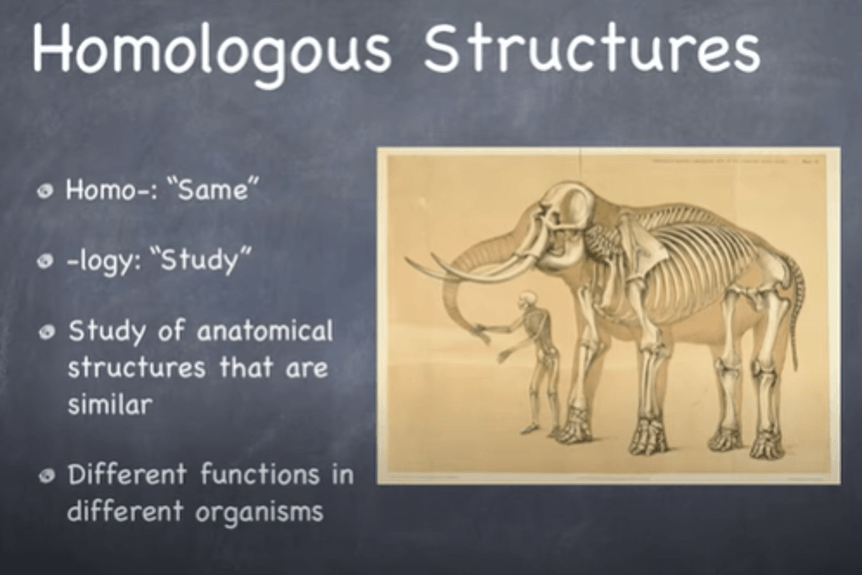
Homologous structures, genes, and developmental pathways Specifically, for anatomical homology, the authors draw the following conclusion: two different animals can be said to have "homologous structures because they were built by homologous genes" through "developmental pathways" that are homologous (p. 41). Homologous Structures - Definition and Examples - Biology Dictionary Homologous structures are organs or skeletal elements of animals and organisms that, by virtue of their similarity, suggest their connection to a common ancestor. These structures do not have to look exactly the same, or have the same function. The most important part, as hinted by their name, is that they are structurally similar. Homologous - Definition and Examples | Biology Dictionary "Homologous," in biology, means a similarity in internal or chromosomal structures. With internal structures, homology indicates organs that have similar positions, structures, or evolutionary origins. It's important to note, however, that organs do not have to have the same function to be homologous. homology/homologous structure - Understanding Evolution homology/homologous structure - Understanding Evolution Inherited from a common ancestor. Human eyes and mouse eyes are homologous structures because we each inherited them from our common ancestor that also had the same sort of eyes. Contrast this with homoplasious and analogous. Inherited from a common ancestor.
Difference Between Homologous and Analogous Structures - Albert Resources Homologous and Analogous Structures Are Derived from Molecular Changes. To conclude, anatomical structures in animals or plants frequently diverge in function due to DNA mutations or epigenetic regulation, resulting in homologous structures in future offspring if the change is favorable for the survival of that organism.
Homologous Structures vs Analogous Structures | Key Differences - YouTube Find classes on topics you are interested in. Follow the link to get a FREE month of Skillshare and access to over 20,000 classes - ⭐ ....
Homologous Structures | Brief Introduction & Examples - iBiologia What are homologous structures: They are defined as the organs or the elements of animals skeletal and organisms that suggest their inheritance from a common ancestor by virtue of their similar properties. These structures do not look exactly similar or the same to each other or have the same functions to do.
Difference Between Homologous and Analogous Structures - VEDANTU Homologous structures can be defined as the organs or skeletal elements of animals and organisms that, by virtue of their similarity, belong to a common ancestor. These structures do not necessarily have to look exactly the same, or have the same function. For example, the arm of a chimpanzee and the arm of a human are homologous.
Homology and Analogy - A lesson in Biology
Homologous Structures: Definition And Examples - Science Trends The term "homologous structures" refers specifically to similar structures found in different species that have a common ancestry or developmental origin. Note that homologous structures don't have to perform the same function in a species, the only requirement is that they are similar in form and exist in species with common ancestry.
What is a homologous structure? - Answers Homologous pairs are called tetrads because these pairs are maid up of a four-part structure. Tetrad literally means a group of four. What it a homolgous structure? Homologous structures - similar...
Difference Between Homologous Structures and Vestigial Structures The key difference between homologous structures and vestigial structures is that homologous structures are the anatomically similar structures found in different organisms that share a common ancestor while vestigial structures are the anatomical structures which have lost their usefulness to an organism.. Homologous structures are vestigial structures are two types of anatomical structures ...
What is the Difference Between Homologous Structures and Vestigial ... Homologous structures refer to organs or skeletal elements of animals that, by virtue of their similarity, suggest their connection to a common ancestor while vestigial structures refer to the structures in an animal that has lost all or most of its original function in the course of evolution.
PDF Difference Between Homologous and Analogous Structures What are Homologous Structures? Homologous structures are the organs or the other structures in different animals which descend from a common ancestor. These structures are anatomically similar, but they may perform different functions. Homologous structures are developed in related organisms since they share a common ancestor.
Difference Between Homologous and Analogous Structures Homologous structures are those morphological features that are found in organisms that evolved from a common ancestor. This means that closely related species often do share homologous traits which are often of similar structure but may have the same or different function. Degree of relatedness:
Homologous Structures: Explanation, Examples, & Traits - Study.com Evolutionary biologists that study genetics of organisms noticed similarities in structures of these organisms even when the function was not the same. These structures are called homologous...
10 Difference Between Homologous And Analogous Structures/Organs With ... A homologous structure is an organ or body part that appears in different animals and is similar in structure and location, but doesn't necessarily share the same purpose. This type of evolution is referred to as divergent evolution. An example of homologous structure is the forelimb of a frog and man seems to be built from same basic design ...
Anatomy, Evolution, and Homologous Structures - ThoughtCo As time passed and technology advanced, homologous structures became more important in deciding the final placement on the phylogenetic tree of life . Linnaeus's taxonomy system places species into broad categories. The major categories from general to specific are kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
























Post a Comment for "40 homolougous structures"